 |
|||||||
 |
|||||||
Arabinogalactan Proteins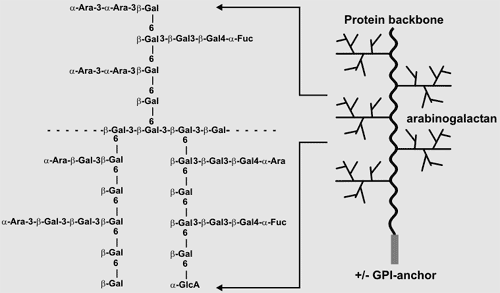 Arabinogalactan proteins are a family of structurally complex proteoglycans (Johnson et al., 2003). The polysaccharide portion of AGPs, which is attached to hydroxyproline residues in the protein backbone, typically accounts for 90% of the molecule and is rich in galactose and arabinose. These polysacchardies are referred to as Type II arabinogalactans. Arabinogalactan proteins are a family of structurally complex proteoglycans (Johnson et al., 2003). The polysaccharide portion of AGPs, which is attached to hydroxyproline residues in the protein backbone, typically accounts for 90% of the molecule and is rich in galactose and arabinose. These polysacchardies are referred to as Type II arabinogalactans.Quantitatively small amounts of AGPs are linked to the plasma membrane by a glycosylphospahtidylinositol (GPI) anchor. Those AGPs not bound to the membrane are present in the apoplast and are readily solubilized with aqueous buffers. AGPs may not be structural components of the wall. Indeed. Nevertheless, there is an increasing awareness that AGPs have important roles in plant growth and development. Moreover, AGPs are present in all land plants including the avascular bryophytes (mosses, liverowrts, and hornworts) and the spore-bearing lycopods and fern allies. Many plant mucilages and gums (e.g. larch arabinogalactan) are composed of Type II arabinogalactans and are a convenient source for the preparation of immunogens. |
Structural Glycoproteins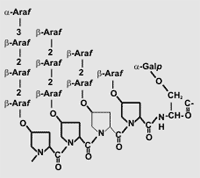 Priamry cell walls typically contain quantitatively small amounts of O-glycosylated proteins (Johnson et al. 2003). These include the hydroxyproline-rich, threonin-rich, and proline-rich glycoproteins. These proteins are glycosylated, albeit to different extents, with arabinose-containing oligosaccharides and with galactose. The Hyp-rich proteins ("extensins") are highly glycosylated with arabinose, arabinobiose, arabinotriose, and arabinotetraose (see figure). Priamry cell walls typically contain quantitatively small amounts of O-glycosylated proteins (Johnson et al. 2003). These include the hydroxyproline-rich, threonin-rich, and proline-rich glycoproteins. These proteins are glycosylated, albeit to different extents, with arabinose-containing oligosaccharides and with galactose. The Hyp-rich proteins ("extensins") are highly glycosylated with arabinose, arabinobiose, arabinotriose, and arabinotetraose (see figure). |
| References Johnson et al (2003) Non-enzymic cell wall (glyco)proteins. In The Plant Cell Wall (Rose JKC ed) Blackwell, pp. 111-154. Back to Top |
|
|
| [Home] | [People] | [Background] | [Research Plan] | [Wall Antigens] | [Antibodies] | [Facilities] | [Links] |
|
|
| A National Science Foundation-funded (Grant No DBI-0421683) research project at The Complex Carbohydrate Research Center of The University of Georgia |